TOROS

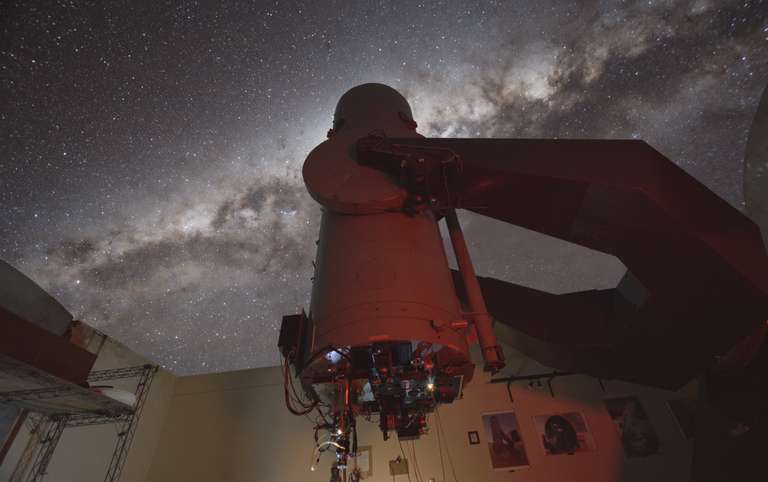
The Transient Optical Robotic Observatory of the South, (TOROS) is being developed as a joint project between University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Universidad Nacional de San Juan, Yerkes Observatory, and Texas A&M University. TOROS detects and characterizes transient astronomical phenomena, including electromagnetic counterparts to gravitational wave sources. The detector had first light at the Felix Aguilar Observatory (FAO) in San Juan Province, Argentina, on September 23, 2024.
Detector
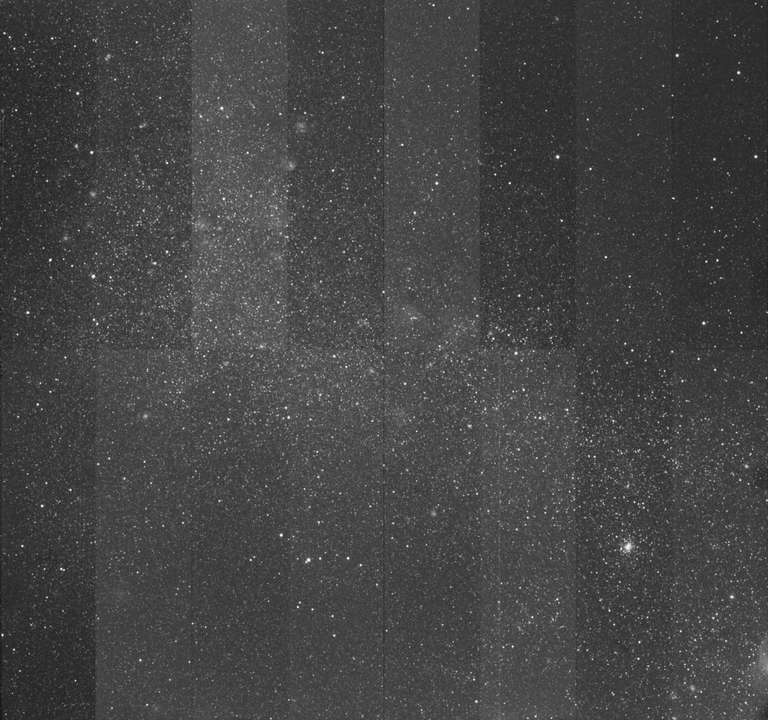
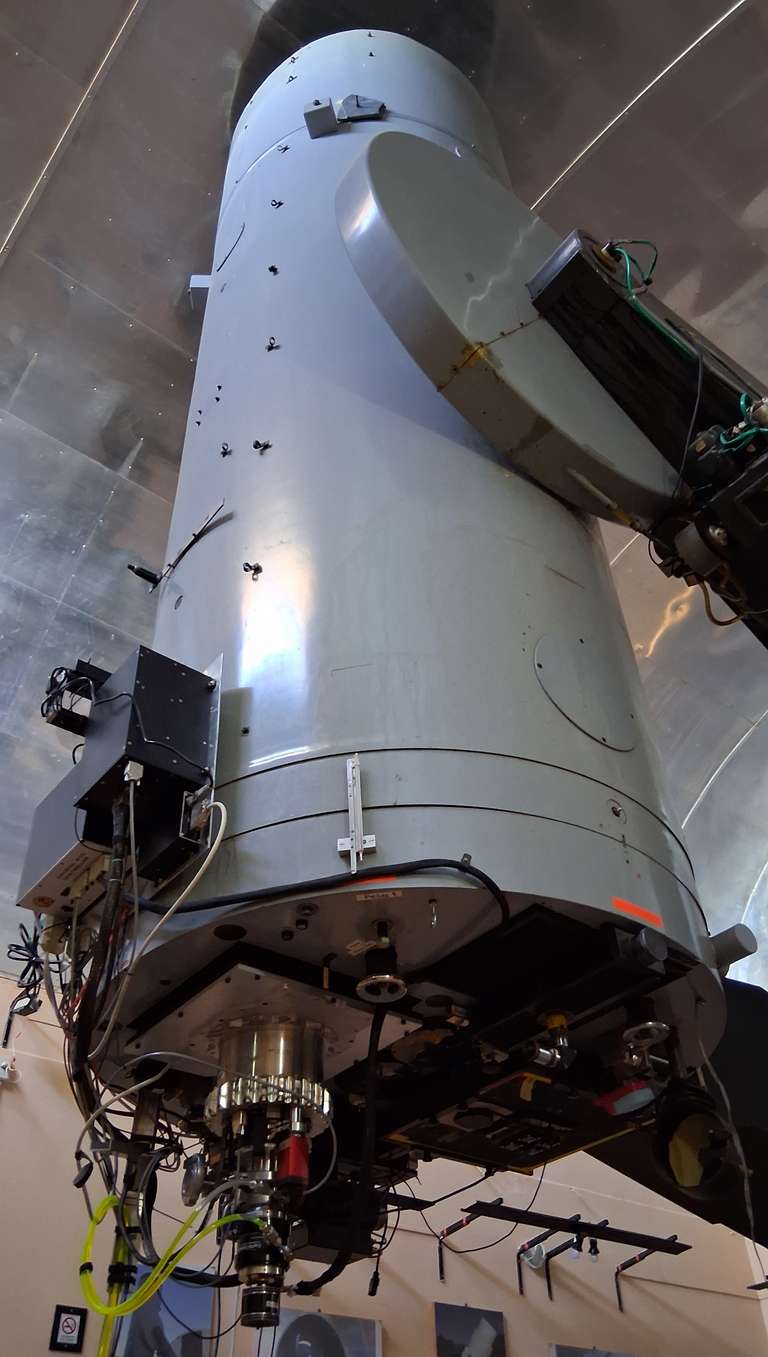
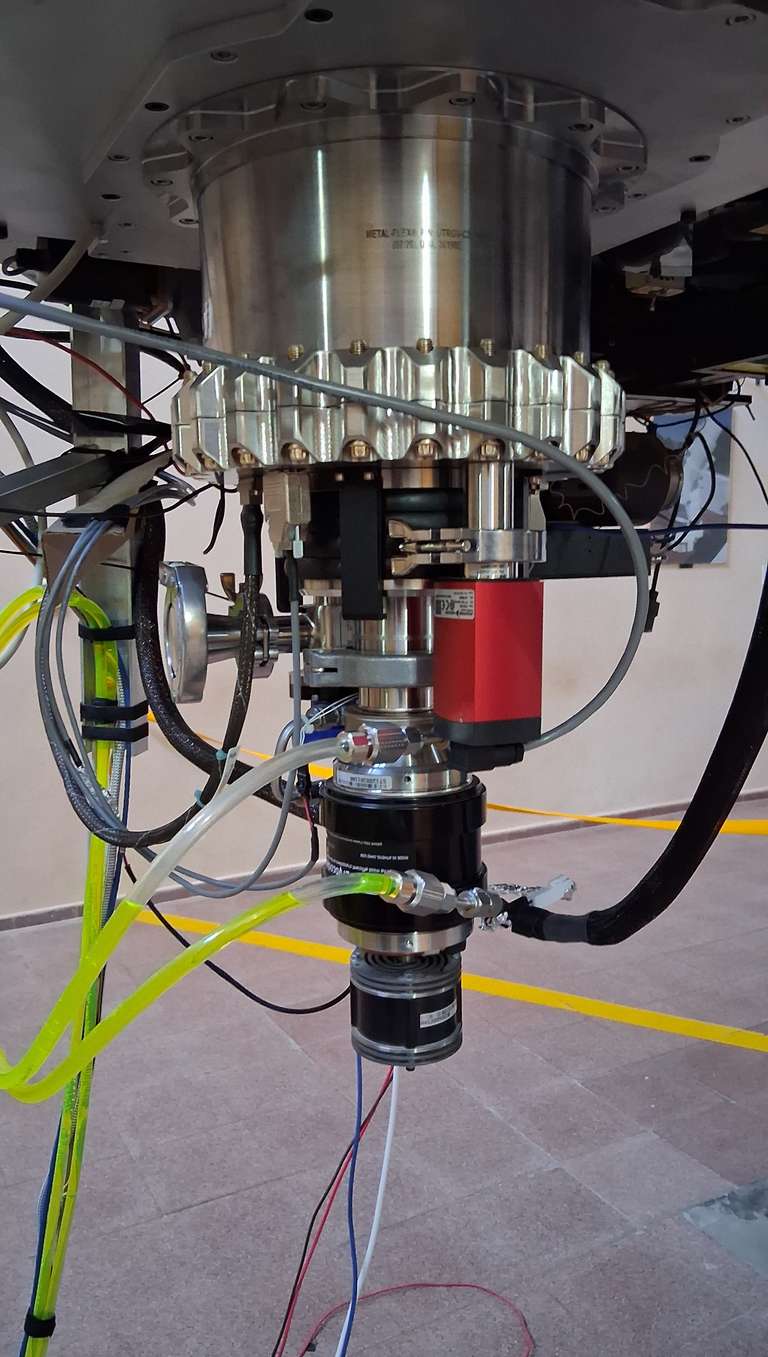
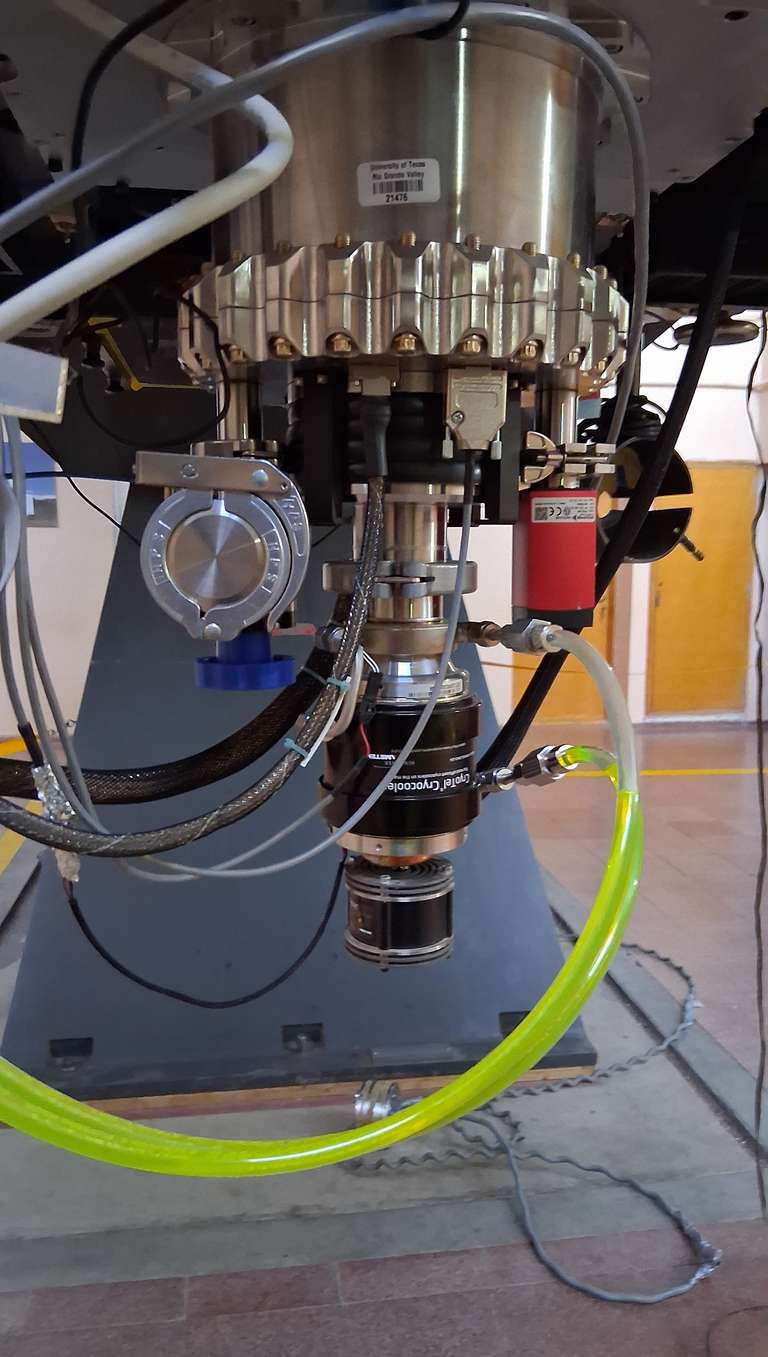
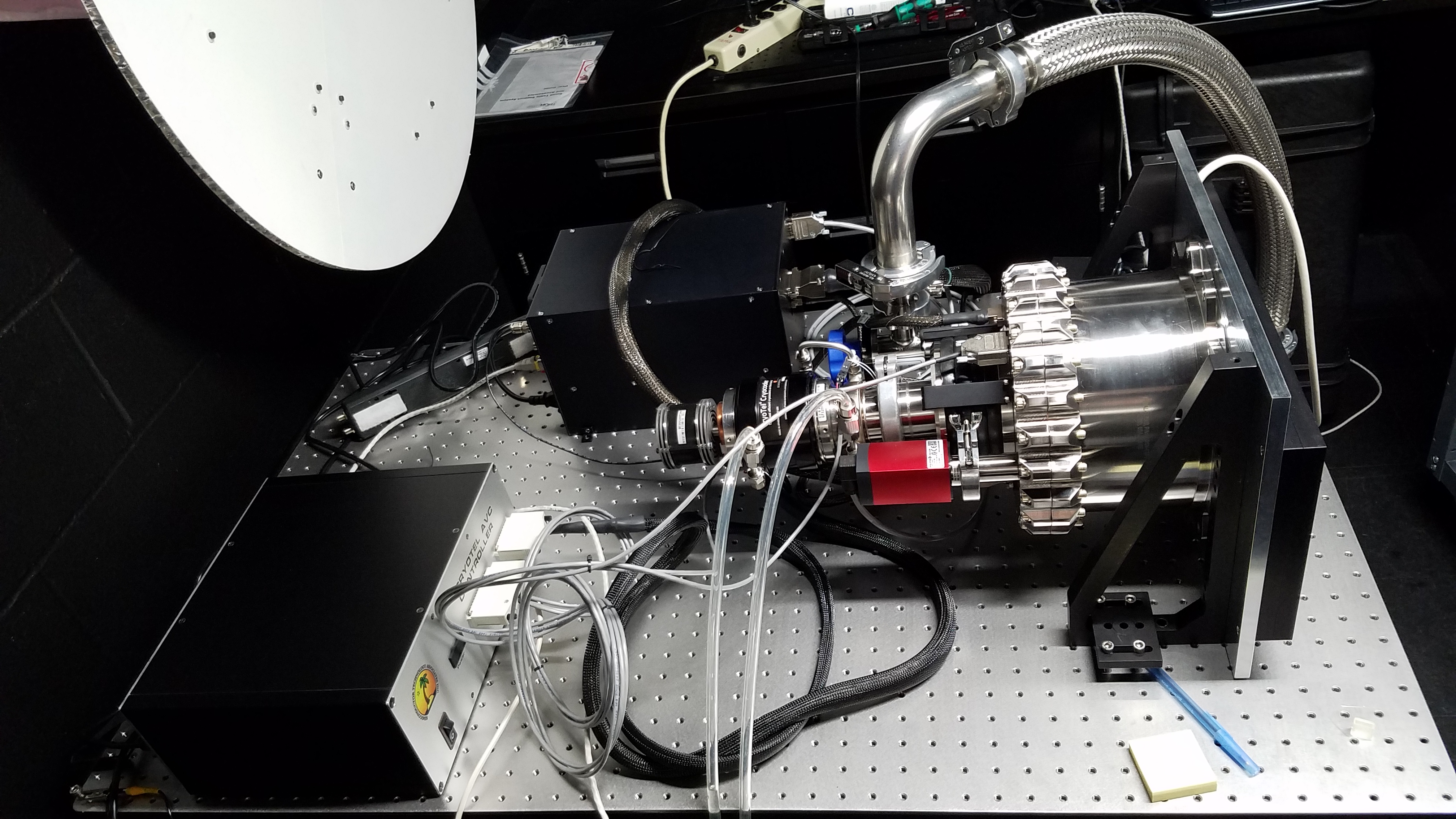
The TOROS detector is a STA1600LN a 10560 x 10560 pixel (9 μm) CCD with a 95.04mm x 95.04mm image area. Plate scale is 0.47”/px with a 1.9 square degree field of view. Its functionality was tested in our lab, and we continue to improve its user interface as needed.
Planewave Corrector
The detector was installed on an Astrograph, but there are plans to install it on a Planewave CDK24 (f/6.5 Corrected Dall-Kirkham).
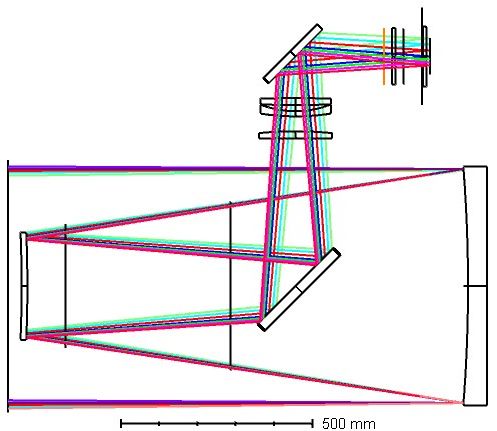
The PlaneWave CDK24 will be modified to include a tertiary mirror, three N-BK7 corrector lenses, a fold mirror, and filters (LSST g,r,i,z, and 550-950 nm broadband).






